Alcohol
Alcohol is legal for people ages 21+. Preventing alcohol use early on, educating youth on the effects of alcohol use, and offering resources on low risk drinking impacts youth health. Be part of the conversation.
Low Risk Drinking
What counts as one drink?
One standard serving is a drink containing 1/2 of an ounce of pure alcohol.
Low Risk Serving Sizes:
Wine (one serving size):
- 4 ounces at 15% ABV (30 proof)
- 5 ounces at 12% ABV
- 10 ounce 6% wine spritzer
Beer (one serving size):
- 12 ounces at 5% ABV
- 8 ounces at 7%
Spirits (one serving size/approx 1 shot):
- 1.5 ounces at 40% ABV (80 proof)
- 1 ounce at 60% ABV (120 proof)
*serving sizes for common alcohol by volume (ABV) rates of different drinks
When NOT to drink:
- Pregnant
- If you are or trying to become pregnant, avoid alcohol use. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders are the leading preventable birth defect in the U.S., affecting 1/20 births.
- Driving
- 32 deaths occur daily in the US as a result of alcohol impaired driving. Impairment lowers ability to judge our own sobriety. Find a designated driver when you drink.
- Using other substances
- Combining substances in the body both increases impairment and reduces your own ability to gauge how impaired you are.
- Taking certain medications
- Common cough syrups, anti-histamines, birth control pills, blood pressure prescriptions, and other meds are complicated by alcohol use. Speak with your doctor about the potential side effects of combining alcohol with your prescriptions.
Why does it matter?
- Alcohol can cause negative short and long-term consequences. This includes trouble concentrating, impulsive behavior, and cancer of the colon, breast, mouth, throat, and liver.
- The World Health Organization reports that there are no safe levels of alcohol use that protect or benefit your health.
- Keep your risks lower by knowing how much alcohol is truly in your drink.
Resources For College Students & Youth
On college campuses across the U.S., many students ages 18 to 24 are taking part in a dangerous activity called binge drinking. Learn more about the dangers associated with binge drinking.
It’s important to understand the side effects of withdrawal or prolonged use, when use turns from recreational to habitual, and the signs of substance misuse. Learn more about substance use in college students.
Full-time college students tend to drink more than others in their age group. Learn more about the habits and dangers of drinking in college students.
To control their drinking, college students need to focus on why they want to drink less, identify their drinking triggers, and develop strategies for drinking less in college. Learn more about the facts of college drinking, why college students drink, and how to drink less.
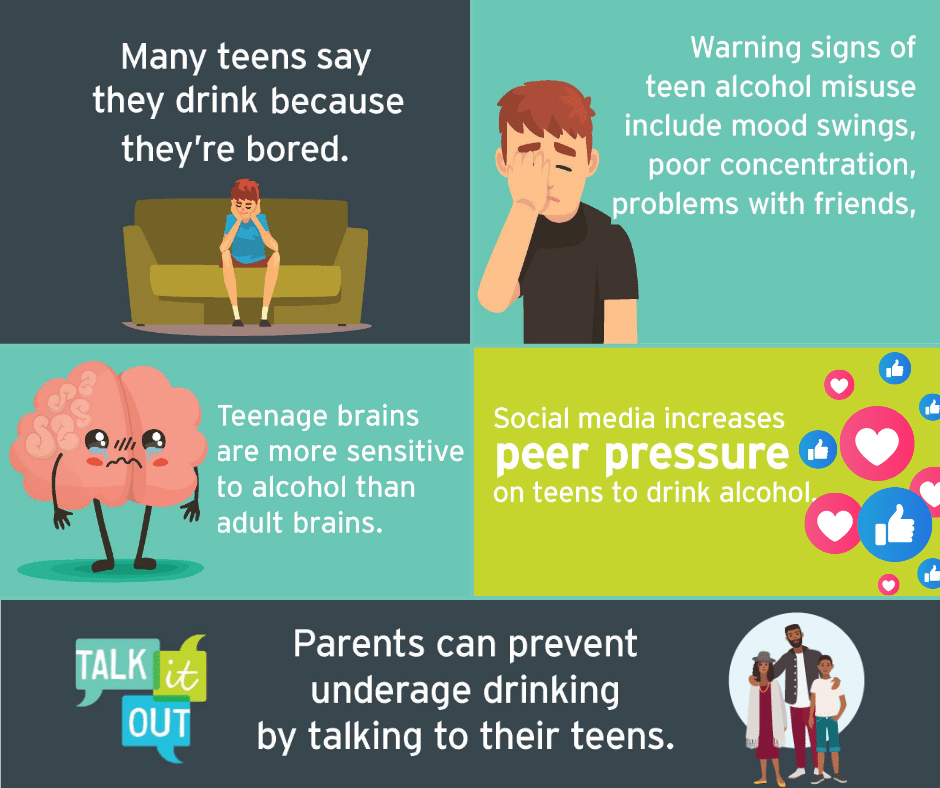
Alcohol is the most widely used substance among America’s youth and can cause them enormous health and safety risks. Learn more about the dangers of underage drinking.
It can be difficult to address underage drinking. Knowing the facts and best to start the conversation is key. Learn more about youth drinking statistics, the dangers of underage drinking, and how to talk to young people about drinking.
Learn about the effects of underage drinking and how you can help prevent it!
*substance use includes alcohol use*
Treatment Resources
Learn about The Department of Health & Human Services’ treatment and recovery resources.
Quick Guide to Maine’s treatment resources.
Find local resources for long term recovery and treatment in Maine.
Find an Alcoholics Anonymous meeting near you.
Information & Resources

Substance Use

Tobacco/Vaping

Mental Health

Alcohol

Cannabis